Projectile Motion
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Projectile_motion
|
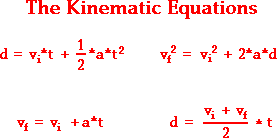
http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/1DKin/Lesson-6/Kinematic-Equations
|
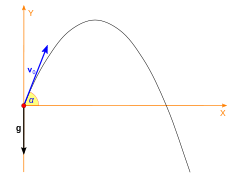
- a= acceleration due
to gravity
|
Projectile Motion describes the motion of the
ball. Whether it's a serve, set, or dig, a
volleyball will always travel in a parabolic
motion. This is because the only force that acts
on the ball after the ball is given an initial
force is gravity assuming that there is no air
resistance. However in an ideal world, the ball
will not travel in a perfect parabolic motion
due to air resistance. For example a float serve
is a serve that puts no spin on ball, and the
ball will travel depending on air flow and can
float in any direction. This serve is used so
that the opponent can not predict where the ball
will be at any instance. In this example other
principles explain this movement such as
Bernoulli's principle. Assuming that there is no
air resistance, with some known values,
kinematic equations can be used to calculate how
far and high the ball will travel.
